Google is working on a new service called Google Translation Center. Just a short while ago, we noticed that “center” had been added to Google’s robots.txt file, and now co-editor Tony Ruscoe discovered the link to the working frontpage... though logging in fails right now. According to the Google explanations on the frontpage and their product overview page, we can see this is meant to be a translation service which offers both volunteers and professional translators... and I suppose at least the professionals will want to get paid. In that regards, the service is in the field of sites like Click2Translate.com (a service by the company which Tony works for, incidentally, and which I’m often using for some of my sites).
Here’s what’s printed as a description on the service’s frontpage:
<<Request translations and find translators
Upload your document and request translations into over 40 languages. [*]
Translate and review translated documents
Create and review content in your language through Google’s free, easy-to-use, online translation tools.>>
And these are the sample screenshots Google shows off in their product introduction:
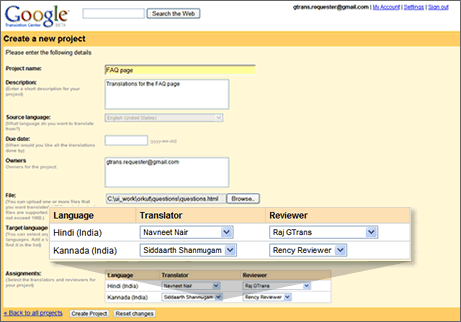
The project creation page. You can provide fields like project name (e.g. “FAQ page”), description, due date and owners. You can set the source and target language, upload a local file to be translated, and assign a translator and a reviewer. “If a translator accepts, you should receive your translated content back as soon as it’s ready,” Google says (note the “if” part, a potentially important difference to paid-only translation services).
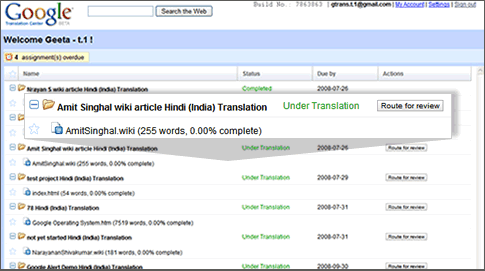
This is what Google calls the translator inbox in their screenshot file name. It looks like the overview page for those approaching the Google Translation Center as a translator. Google says, “Passionate about bringing content into your language? Browse through Google Translation Center to find open translation requests into your language. Accept translation requests and use Google translation tools to provide quick, high-quality translations.” In this view, you can find out the number of assignments, and the completion status for each.
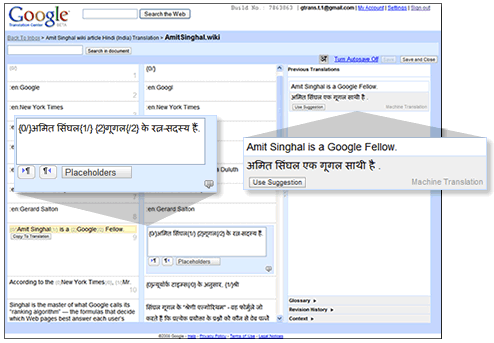
The part Google calls the translator workbench. In this view, the translator sees the source text and the translation in progress side-by-side. An option on top toggles auto-saving. A third column offers a couple of helper tools for the translation, like a revision history, a glossary, or a history of previous translations.
More than an all-in-one stop for paid translations as some of the competing services in this field, the Google Translation Center looks like it aims to be a marketplace coordinator and tool provider. Just how Google could make money with this is another question. Google often goes for ads; in this system, one might think getting commissions for paid jobs would be an option, but there’s a part in the terms and conditions of the service which makes me wonder if there will be such a thing – Google says (my emphasis):
<
I’m also curious if volunteers will get paid, too, as one might think it’s not like everyone is waiting to do free translations... unless they identify with a site or some content re-use is allowed (like an open source project, perhaps, or a Creative Commons licensed article). If Google decides to provide a rating system, though, then volunteering for projects may have the side-effect of increasing one’s status within the service.
Another interesting aspect is how Google will handle the service’s feature to match current translations with previous ones. Tony says, “This sounds like what the industry calls a ’Translation Memory’. Usually, the client would pay for a translation memory and own it since they paid for the translations.” Tony adds that if Google may plan to add something like a “global Translation Memory,” then this could raise the questions whether or not customers end up paying for pro translators to find their translation memory be re-used by other companies. Another issue of discussion will likely be the translation quality, by and large; just imagine someone volunteering to sneak in insults or spam. From Google’s FAQ on this:
<<Does Google provide guarantees on the quality of the services provided by Google Translation Center?
No. Translations created in Google Translation Center are purely between the translation requester and the translators.>>
And as the terms of service argue, “Google will not” be “involved in resolving any disputes between you and any third party participant(s) related or arising out of your use of Google Translation Center”. But let’s wait and see. Judging from my past translation jobs as a webmaster – give the service a data file containing all your content strings, plug it back in later on and suddenly have a multi-language website – this is definitely an interesting and highly useful field. Right now, according to the FAQ, “Google Translation Center is in limited release through Google’s Trusted Tester Program” which gives “friends and family members of Google employees a chance to test-drive our early beta, prior to release. Later, anyone can sign up to request and provide translations through Google Translation Center.”





























